Petrochemical
5,000 Tons/Year Polylactic Acid Fiber Project of Siping City
1. Introduction to the Project
1.1 Project background
1.1.1 Product introduction
Polylactic acid fiber is an innovative synthetic fiber derived from starch rich crops such as corn, wheat, and sugar beets. It is made through the fermentation process, converted into lactic acid, condensing and melt spinning processes. This type of fiber not only has renewable raw materials and is easy to grow, but its waste can also be completely biodegraded in the natural environment. Under the action of microorganisms in soil or seawater, polylactic acid fibers can be decomposed into carbon dioxide and water, and cannot release harmful gases when burned, making it an environmentally friendly and sustainable material. The fabric made of polylactic acid fiber has excellent tactile and drape properties, strong UV resistance, low flammability, and excellent processing performance. It is applicable for various clothing fields, including fashion, casual wear, sports equipment, and hygiene products, demonstrating its wide application potential.
1.1.2 Market prospect
(1) Current situation of polylactic acid fiber market
With the increasing global awareness of environmental protection and the demand for sustainable development, the market demand for polylactic acid, as a biodegradable plastic derived from renewable resources, has experienced explosive growth. Especially in the fields of packaging, disposable tableware, agricultural film, textiles, and medical supplies, the application of polylactic acid is gradually expanding. According to data from market research institutions, polylactic acid fibers achieved significant real growth during 2020 - 2024. Especially during 2021- 2022, due to the surge in global demand for environmentally friendly materials, the production and sales volume of polylactic acid fibers have doubled. By 2024, the global market size of polylactic acid fibers has reached an unprecedented level. According to statistics, the demand for polylactic acid in the domestic market reached about 400,000 tons in 2024, demonstrating a strong market growth momentum. Globally, especially major economies such as China, the EU, and the United States are increasing their support for biobased materials, further promoting the development of the polylactic acid market.
Looking ahead, it is expected that the market for polylactic acid fibers will continue to maintain strong growth momentum until 2030. With the continuous improvement of consumer environmental awareness and the continuous support of the government for the environmental protection industry, the market demand for polylactic acid fiber, as a new type of fiber material with significant environmental advantages, will continue to expand. Meanwhile, with the continuous improvement of production processes and the gradual reduction of costs, the application fields of polylactic acid fibers will also be further expanded, providing strong guarantees for their long-term stable growth in the market.
The implementation of restrictive policies on disposable plastic products by multiple governments, as well as support for biobased materials, has provided broad development space for the polylactic acid market. For example, China’s 14th Five-Year Plan clearly sets the goals of green and low-carbon development and ecological civilization construction, providing policy guarantees for the development of biodegradable materials such as polylactic acid. The EU’s “European Green Deal” and multiple environmental initiatives in the United States also emphasize reducing plastic use and promoting the development of bio-based materials. These policies not only restrict plastics, but also directly promote the expansion of the polylactic acid market through subsidies, tax incentives, etc.
In recent years, the production cost of polylactic acid has been reduced and its performance has been significantly improved by optimizing fermentation efficiency, improving polymerization processes, and diversifying raw materials. For example, using non grain crops as raw materials not only reduces dependence on food resources, but also broadens the sources of raw materials and reduces raw material costs. Meanwhile, through modification technology, the performance of polylactic acid materials in terms of heat resistance and toughness has been optimized, expanding their possibilities in high-end application fields.
By now, the polylactic acid fiber market is gradually developing and growing. The preparation process of polylactic acid fiber is constantly improving, and the production cost is effectively reduced, making large-scale production and application possible. The performance of polylactic acid fibers has also been improved, including improvements in strength, durability, and antibacterial properties. In the fields of textile, medical, packaging, etc., polylactic acid fibers are gradually replacing traditional materials and becoming the new favorite of the market.
(2) Market prospect of polylactic acid fiber
With the continuous improvement of consumer environmental awareness and the global pursuit of sustainable development, the market demand for polylactic acid fibers is steadily increasing. In the textile industry, polylactic acid fibers are widely used to produce various environmentally friendly clothing and home textile products; In the medical field, its unique biocompatibility makes it an ideal choice for medical devices and drug carriers; In the packaging industry, biodegradable packaging materials made from polylactic acid fibers are gradually replacing traditional plastic packaging, helping to reduce “white pollution”. These applications not only promote the green transformation of related industries, but also contribute to global sustainable development.
The market prospect of polylactic acid fiber is extremely broad, mainly due to its environmental characteristics and continuous improvement of production processes.
1. Market demand growth
With the increasing global awareness of environmental protection, the market demand for polylactic acid fiber as a biodegradable material continues to grow. Especially in the fields of healthcare, environmental protection, and daily necessities, the application prospects of polylactic acid fibers are very wide. In the medical field, polylactic acid fibers are mainly used for surgical sutures, drug release carriers, and tissue engineering scaffolds. Furthermore, polylactic acid fiber also has excellent wearing comfort and moisture absorption, applicable for underwear, shirts, sportswear, and household items.
Textile industry demand: Polylactic acid fiber has become an ideal choice for producing high-end clothing and home textiles due to its excellent moisture absorption, breathability, and comfort. With the continuous pursuit of high-quality life by consumers, the demand for polylactic acid fiber products is expected to steadily increase.
Medical and health products: The application of polylactic acid fibers in the field of medical and health products is becoming increasingly widespread, such as surgical sutures, medical dressings, etc. With the advancement of medical technology and the increasing demand for healthcare, the market demand for polylactic acid fiber will further expand.
Packaging industry demand: Polylactic acid fiber can be used to make various packaging materials, such as food packaging bags, drug packaging bags, etc. Due to its excellent biodegradability and compliance with environmental requirements, it has broad market prospects in the packaging industry.
2. Expansion of application areas
The application fields of polylactic acid fibers are constantly expanding. By now, polylactic acid fibers are mainly used in packaging materials, medical supplies, and environmental protection fields. With the advancement of technology, the performance of polylactic acid fibers is constantly improving, which is expected to be widely used in high-performance fibers, engineering plastics, and other fields in the future. For example, polylactic acid non-woven fabric, as a packaging material, not only has excellent biodegradability, but also has excellent mechanical properties, applicable for packaging needs of various shapes and sizes.
3. Policy support
Multiple countries and regions around the world are continuously increasing their support for biobased materials. For example, China’s 14th Five-Year Plan clearly sets the goals of green and low-carbon development and ecological civilization construction, providing policy guarantees for the development of biodegradable materials such as polylactic acid. The “European Green Deal” of EU and multiple environmental initiatives in the United States also emphasize reducing plastic use and promoting the development of biobased materials. These policies not only restrict plastics, but also directly promote the expansion of the polylactic acid market through subsidies, tax incentives, and other means.
1.1.3 Technical analysis
This project intends to introduce mature technology, and the production process is all compound production, which is mature and reliable, with a simple process, low raw material consumption, and good product quality.
1.1.4 Advantageous conditions of project construction
(1) Policy advantages
The policies for generating polylactic acid fiber projects mainly include the following aspects:
Subsidies and tax incentives: The Chinese government has provided strong support for the research and industrialization of biobased materials, including direct funding subsidies, R&D funding support, tax reductions, and other preferential policies for polylactic acid projects. These measures aim to reduce production costs for enterprises, promote technological progress and industrial upgrading.
Plastic restriction policy: Since 2020, many parts of China have implemented strict plastic restriction policies, restricting the use of disposable plastic products, especially plastic bags and tableware. This policy directly increases the demand for biodegradable plastics, including polylactic acid, and brings broad market space to the polylactic acid industry.
(2) Industrial advantages
Lishu County, Siping City, has obvious industrial advantages. With the national level (food) agricultural and livestock product processing new industrialization industry demonstration base, provincial building materials industry park, and Jinshan gas field as platforms, Lishu County has initially formed four pillar industries of food, building materials, energy, and services. The raw materials required for the production of polylactic acid fibers in the project all come from the surrounding market, with sufficient supply, convenient transportation, and reliable cooperative manufacturers and supply channels, making it easy to purchase.
(3) Location advantages
Siping is located in the southeast of Jilin Province, adjacent to the Changbai Mountains to the east, the Khorchin Grassland to the west, Shenyang and Dalian to the south, and Changchun and Harbin to the north. Located in the central area of Northeast Asia, on the development axis of revitalizing Harbin Dalian in Northeast China, it is an important strategic pivot city of the Harbin Great Wall urban agglomeration and a bridgehead for Jilin Province to open up to the south. Since ancient times, it has been a battleground for military strategists, and now it is showing a trend of winning for businesses.
The Xinkai District is located on the first level development axis of revitalizing Harbin University in Northeast China. It is 80 km away from Changchun, 120 km away from Longjia Airport, 190 km away from Shenyang, 230 km away from Jitaoxian Airport, 380 km away from Yingkou Port, and 580 km away from Dalian Port. Several major transportation arteries in the Northeast region, including the Beijing-Harbin Railway, Harbin-Dalian High-speed Railway, National Highway 102, Jiji-Shuangliao Expressway, Harbin- Dalian Expressway, and Ji’an-Dalian Expressway, all pass through the area. There are 2 railway stations, 8 railway dedicated lines, and 3 highway exits in the surrounding area. Siping Station is one of the 18 freight marshalling yards in China’s railways, an important transportation hub in Northeast China, with convenient transportation of raw materials and products.
(4) Talent advantages
Xinkai District collaborated with Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences to establish a science and technology innovation center platform, collaborated with Xi’an Jiaotong University National Technology Transfer Center to establish Xi’an Jiaotong University Siping Center, and collaborates with Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics to establish Siping Research Branch; It has unique advantages in promoting the R&D of new chemical materials and the transformation of achievements. Research institutes and universities such as Changchun Institute of Chemical Engineering Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Jilin University, Harbin Institute of Technology, Dalian Institute of Technology, Northeast Normal University, Jilin University of Chemical Technology, etc. provide talent and technological support for enterprises; Meanwhile, it can also provide technology services, technology transfer, achievement transformation, fund introduction, and consulting services for enterprises in the park. Several universities, including Siping Vocational University, Jilin Engineering Vocational College, and Lishu Vocational High School, provide employment security.
1.2 Contents and scale of project construction
The overall planning area is 12,000 ㎡, with the construction of production areas, office and living areas, warehouse areas, and the purchase of production, testing, and experimental equipment. Annual production of 5,000 tons of polylactic acid fiber.
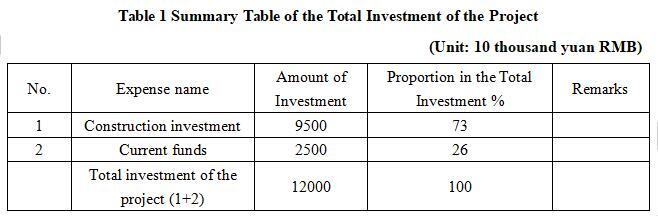
1.3 Total investment of the project and capital raising
The total investment of the project is 120 million yuan, including the construction investment of 95 million yuan.
1.4 Financial analysis and social evaluation
1.4.1 Main financial indexes
After the project reaches the production capacity, its annual sales revenue will be 110 million yuan, its profit will be 23 million yuan, its investment payback period will be 6.5 years (after the tax, including the construction period of 1.5 years) and its return on investment will be 20%.
Table 2 List of Major Indexes for Forecast of Financial Benefits
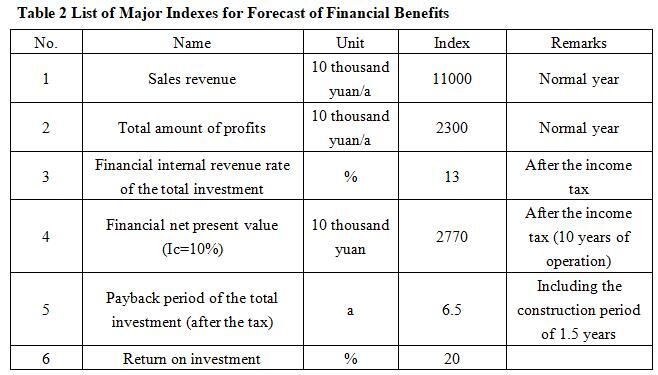
Note: “10 thousand yuan” in the table is in RMB
1.4.2 Social evaluation
The social benefits of the project of producing polylactic acid fibers are mainly reflected in the following aspects:
Environmental benefits: Polylactic acid fiber is made from starchy agricultural products such as corn, wheat, sugar beets, etc. through being fermented to produce lactic acid, and then condensed and melt spun. This production process not only has renewable raw materials, but also produces pollution-free products that can be completely degraded, helping reduce plastic pollution and protect the environment.
Resource conservation: The production of polylactic acid fibers uses agricultural waste and renewable resources to reduce dependence on non-renewable resources such as oil and helping to alleviate the problem of resource depletion.
Health and safety: Polylactic acid fiber is non-toxic and odorless, with good biocompatibility and degradability, widely used in medical fields such as surgical sutures and bandages, reducing environmental pollution caused by medical waste.
Promoting agricultural development: The production of polylactic acid fibers promotes to use agricultural waste, increase the added value of agricultural resources, and contribute to sustainable agricultural development.
Promoting technological innovation and industrial upgrading: The production of polylactic acid fibers requires advanced fermentation technology, extraction technology, and polymerization technology, promoting technological innovation and industrial upgrading in related fields.
Enhancing employment opportunities: The construction of the polylactic acid fiber project requires a large number of R&D, production, and sales talents, creating a large number of job opportunities and promote local economic development.
Enhancing public environmental awareness: The widespread use of polylactic acid fibers helps to raise public awareness and usage of environmentally friendly materials, promoting the overall environmental awareness of society.
1.5 Cooperative way
Sole proprietorship, joint venture and cooperation.
1.6 What to be invested by the foreign party
Funds, other ways can be discussed in person.
1.7 Construction site of the project
Siping New Industrial Economic Development Zone Ecological Chemical Industrial Park
1.8 Progress of the project
The project proposal has been prepared
2. Introduction to the Partner
2.1 Basic information of unit
Name: Management Committee of Siping New Industrial Economic Development Zone
Address: Guojiadian Town, Lishu County, Siping City, Jilin Province
2.2 Overview of unit
Jilin Siping New Industrial Economic Development Zone is a provincial-level economic development zone officially approved by the Jilin Provincial Government on December 7, 2016. It is an important carrier of new industry in Siping City. The new development zone is located in the northeast of Siping City, 10 km away from the city center, with a planned area of 30.71 k㎡, including four parks: Ecological Chemical Park of 12.15 k㎡, Logistics Park of 2.89 k㎡, Building Materials Park of 3.91 k㎡, and Equipment Manufacturing and Urban-Rural Integration Zone of 11.76 k㎡. There is a provincial-Level characteristic ecological chemical town in the area. The zoning plan, land use plan, industrial plan, safety assessment, and environmental impact assessment of the newly opened zone have been approved, and the safety risk assessment of the chemical industrial park has been passed. In 2023, the safety risk assessment of the chemical industrial park was rated as national Level D.
2.3 Contact method
Contact unit: Investment and Operation Bureau of Siping New Development Zone
Contact person: Yu Quan
Tel: +86-13844482777
E-mail: xkqtzyxj@126.com
Contact method of the city (prefecture) where the project is located:
Contact unit: Siping Municipal Economic and Technical Cooperation Bureau
Contact person: Wen Dacheng
Tel: +86-434-3260536
E-mail: spjhjjhk@163.com


